Welcome to “Pills of Technique”. These posts are dedicated to those who know very little about it and aim to present simple notions as briefly as possible.
Along this short post there are links to some websites where you can learn more about the topics discussed.
Images are the property of the respective websites mentioned in the post
1
How a Dipole Antenna Works
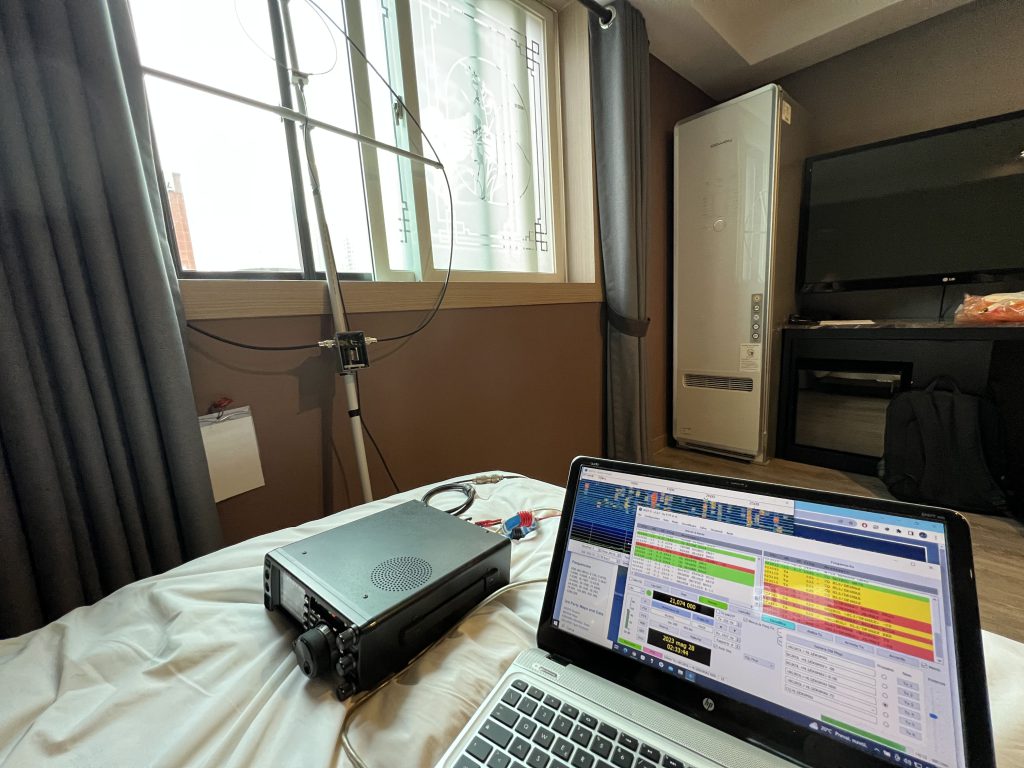
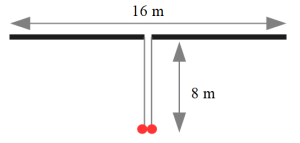
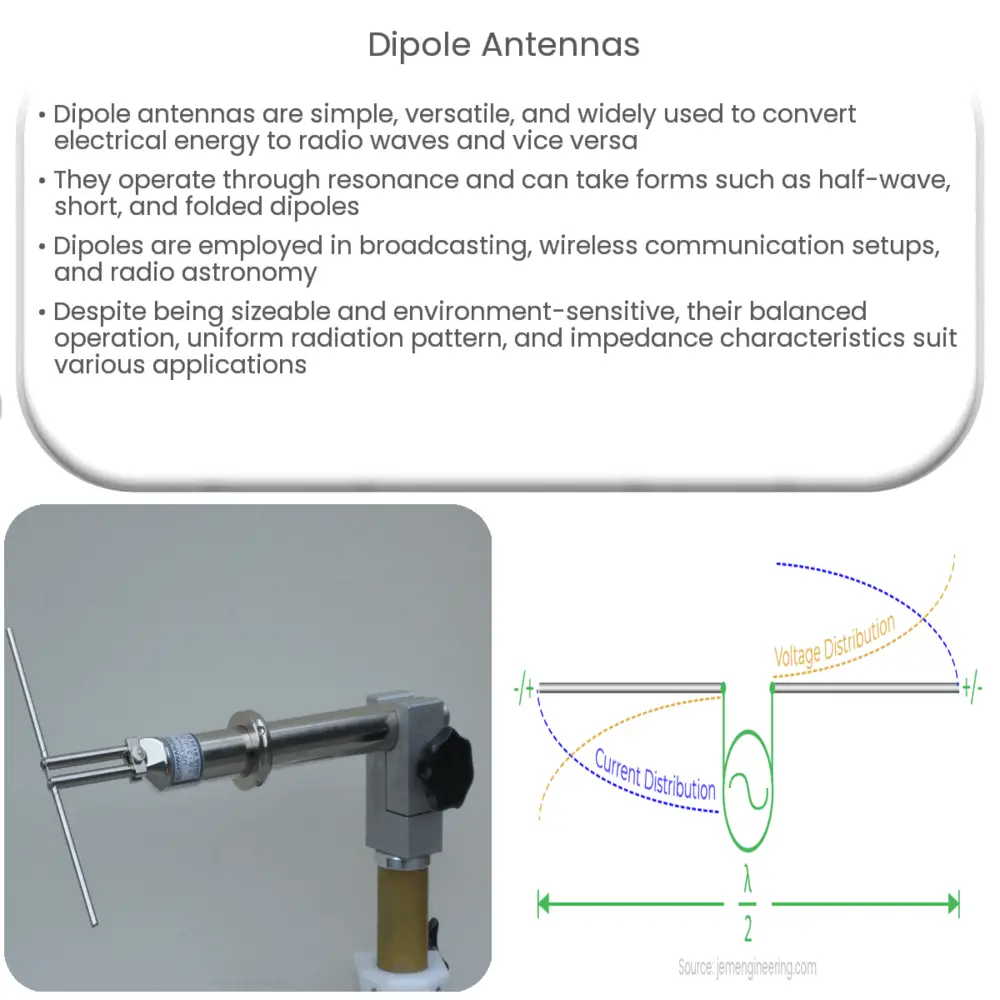
Dipole antennas are one of the most basic and common types of antennas. They are used in a wide variety of applications, including radio and television broadcasting, amateur radio, and cellular communications. Dipole antennas are relatively simple to construct and operate, and they are effective at transmitting and receiving radio waves.
2
What is a dipole antenna?

- A dipole antenna is a type of antenna that consists of two metal elements, typically straight and thin, arranged in a parallel configuration.
- The length of the elements is approximately half the wavelength of the radio waves that the antenna is designed to transmit or receive.
- The elements are connected to a feed point, which is typically a coaxial cable.
- The feed point is where the radio signal is applied to the antenna.
3
How does a dipole antenna work?
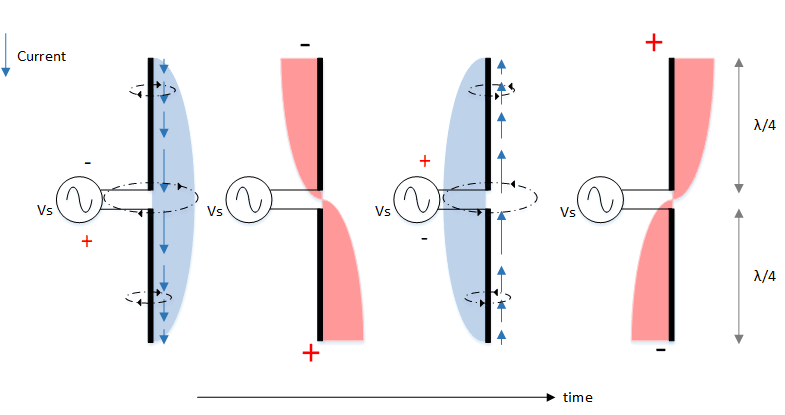
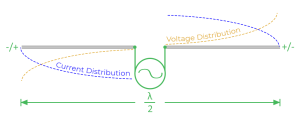
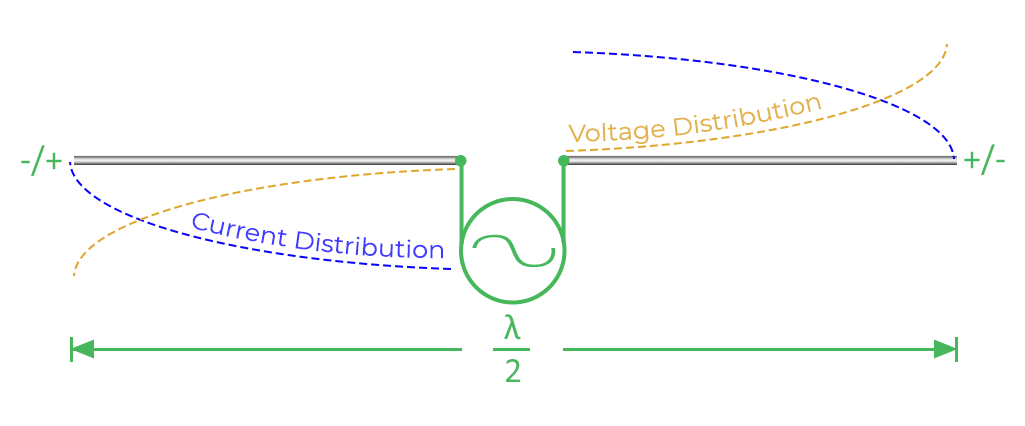
- When a radio signal is applied to the feed point of a dipole antenna, a current flows through the elements.
- This current creates a fluctuating magnetic field around the antenna.
- The fluctuating magnetic field generates a radio wave that propagates away from the antenna.
- The radio wave is strongest in the direction perpendicular to the elements of the antenna.
4
Factors affecting the performance of a dipole antenna
- The performance of a dipole antenna can be affected by several factors, including:
- The length of the elements: The length of the elements should be approximately half the wavelength of the radio waves that the antenna is designed to transmit or receive.
- The material of the elements: The elements are typically made of copper or aluminum, which are good conductors of electricity.
- The diameter of the elements: The diameter of the elements should be large enough to support the current that flows through them.
- The position of the antenna: The antenna should be positioned in an open area away from obstacles that could reflect or absorb the radio waves.
5
Applications of dipole antennas
- Dipole antennas are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Radio broadcasting: Dipole antennas are used by radio stations to transmit their signals.
- Television broadcasting: Dipole antennas are used by television stations to transmit their signals.
- Amateur radio: Dipole antennas are used by amateur radio operators to communicate with each other.
- Cellular communications: Dipole antennas are used by cellular phone towers to transmit and receive signals from cell phones.
- Wi-Fi: Dipole antennas are used in Wi-Fi routers to transmit and receive signals from Wi-Fi devices.
6
Advantages of dipole antennas

Dipole antennas offer several advantages, including:
- Simplicity: Dipole antennas are relatively simple to construct and operate. They can be made from a few simple materials, and they do not require any complex electronics.
- Effectiveness: Dipole antennas are effective at transmitting and receiving radio waves. They have a wide bandwidth, which means that they can be used to transmit and receive a wide range of frequencies.
- Low cost: Dipole antennas are relatively inexpensive to manufacture. This makes them a good choice for applications where cost is a major concern.
- Robustness: Dipole antennas are robust and can withstand harsh weather conditions. They are also relatively resistant to damage from shock and vibration.
- Versatility: Dipole antennas can be used in a wide variety of applications. They are used in everything from radio and television broadcasting to amateur radio and cellular communications.
7
Disadvantages of dipole antennas
Dipole antennas also have some disadvantages, including:
- Low directivity: Dipole antennas have a low directivity, which means that they radiate radio waves in a wide area. This can be a disadvantage if you need to transmit or receive a signal in a specific direction.
- Low gain: Dipole antennas have a low gain, which means that they produce a relatively weak signal. This can be a disadvantage if you need to transmit a signal over a long distance.
- Sensitivity to interference: Dipole antennas are sensitive to interference from other sources of radio waves. This can be a problem in areas with high levels of radio noise.
8
Conclusion
Dipole antennas are a versatile and useful type of antenna that is used in a wide variety of applications. They offer several advantages, including simplicity, effectiveness, low cost, robustness, and versatility. However, they also have some disadvantages, including low directivity, low gain, and sensitivity to interference. When choosing a dipole antenna, it is important to consider the specific application and the trade-offs between the advantages and disadvantages.
In the next “Pills of technique” post we will see how to build one.